MXScandinavia dyno tested shim factor equivalent stacks on Thumper Talk to evaluate the accuracy of shim factor scaling. By shim factor theory, a stack of 4x40.3 face shims is 3.8% softer than a stack of 14x40.2 shims.
Dyno test results shows the actual difference was approximately double that at 7.7% (data points). Shim ReStackor analysis of the two shim stack configurations shows the same thing (lines).
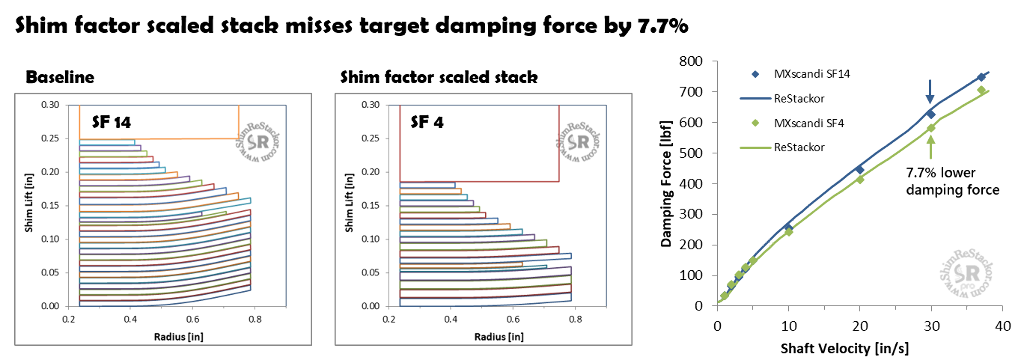
MXScandinavia dyno testing of shim factor equivalent shim stacks shows 7.7% less damping force
Shim factor dyno testing
The baseline 14x40.2 stack has a shim factor of 112. The shim factor could be matched using 4x40.3 face shims (sf=108) plus four additional 4x40.1 shims (sf=4) to bring the shim factor sum to 112.
Running Shim ReStackor with the additional 4x40.1 face shims shows the damping force matches the target 14x40.2 baseline shim stack.

Adding four 40.1 face shims matches the baseline shim stack shim factor and damping force
Running the above calculations with the setup reversed to locate the additional 4x40.1 shims behind the thicker face shims shows the damping force is 2% lower.
The damping force difference is created by shim friction. Locating the 4x40.1 shims on the face of the shim stack heavily loads the interface between each shim. The high load increases friction making the shim stack stiffer.
Locating 40.1 shims behind the thicker 40.3 face shims allows the thicker face shims to transfer a portion of the load directly into the shim stack clamp. The reduced load on the thinner 40.1 shim interfaces reduces friction making the shim stack and damping softer.

Reversing setup reduces damping force due to shim friction effects
Shim ReStackor FEA calculations compute the forces acting on the top and bottom surface of each shim. Quantifying the shim interface forces allows accurate calculation of shim friction and its effect on shim stack stiffness and damping force.
Adding a thicker shim to the shim stack taper section, changes the shim interface forces for all of the shims below, which alters the friction forces and the effective shim stack stiffness. Shim ReStackor FEA calculations are designed to correct for those effects.
