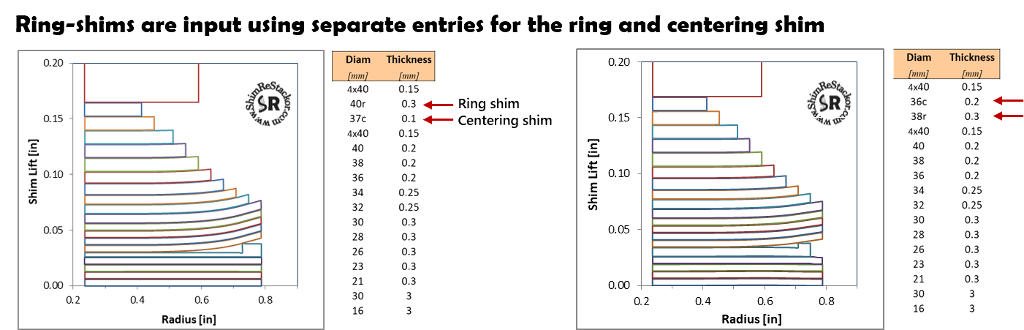
Ring shims have two parts: a centering shim and a thicker outside ring shim. The ring shim preloads the shim stack against the valve face requiring higher pressures to crack the shim stack open.
Shim ReStackor requires two inputs for ring shims. The centering shim is marked with the letter “c” and the thicker ring-shim is marked in a separate input with the letter “r”.
The centering shim can be listed first or second, the order does not matter.
Preload produced by the ring-shim can be tuned by changing the ring-shim thickness or the centering shim thickness. Preload can also be changed moving the ring shim up or down in the stack or by changing the ring shim diameter.
Ring shim tuning
Preload produced by ring-shims significantly increase damping force everywhere across the speed range. Chucking a ring-shim on an existing shim stack to see what it “feels” like on a test ride will give the result of “too stiff” everywhere.
To make ring-shims useful the shim stack has to be re-tuned to work with the ring-shim preload and increased low speed damping.
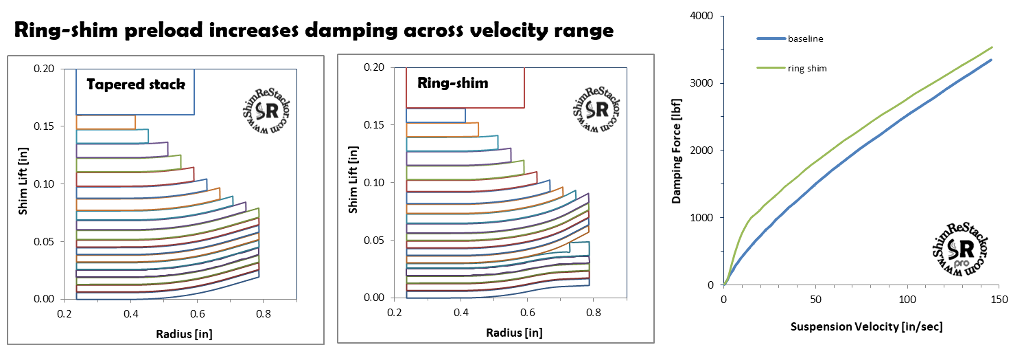
Increased low speed damping
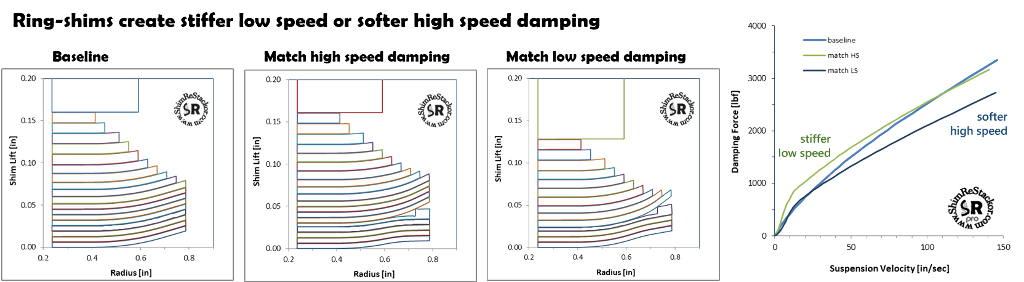
Ring-shims are typically used to increase low speed damping. The example below softens the shim stack taper using thinner shims to compensate for the ring-shim addition.
The result is stiffer damping at low speed and the same damping at high speed.
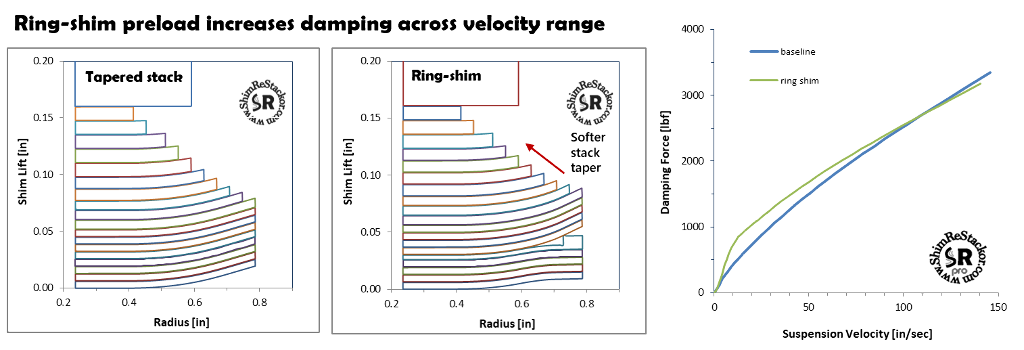
Reduced high speed damping
Ring shims can be tuned the other way around to soften high speed damping.
Adjusting ring-shim preload on a soft shim stack matches the low speed damping force of the original baseline stack.
When pushed to high speed, the softer shim stack produces less damping force giving the result of matched low speed damping and softer high speed.
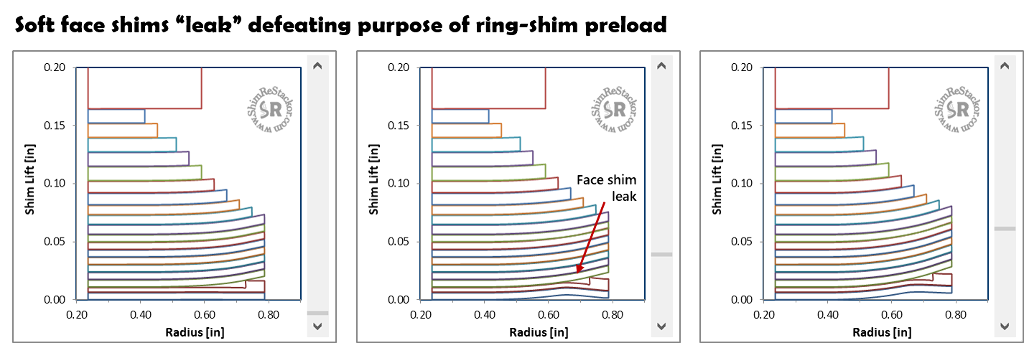
Face shim distortion
Ring-shim preload holds the outside edge of the shim stack closed. When used with thin face shims the clamped outside edge allows the face shims to distort and leak along the valve port side. The leak vents low speed damping partially defeating the purpose of the ring-shim.
That situation can be avoid using multiple or thicker face shims.
The stack deflection graphic in Shim ReStackor shows when the face shim stiffness is inadequate as the example below demonstrates.